Introduction to Chemistry: Structures and Solutions
Duke University
Go to this Course: Introduction to Chemistry: Structures and Solutions
Hello Friends in this article i am gone to share Coursera Course: Introduction to Chemistry: Structures and Solutions Week 1 Exercises Quiz Answers with you..
Week 1 Exercises Quiz Answers
Question 1)
What is the frequency of a photon with a wavelength of 781 nm. Report your answers to three significant digits.
The frequency is = _________ s-1
Answers:
Question 2)
What is the energy of a photon with a wavelength of 260 nm. Report your answers to three significant digits.
The energy is _________ J.
Answers:
Question 3)
Which electron transition in a hydrogen atom would absorb the photon of greatest frequency?
n = 3 to n = 1- n= 12 to n= 6
- n = 1 to n= 4
- n = 35 to n = 2
- n = 2 to n= 9
n = 6 to n = 2
Question 3)
Which electron transition in a hydrogen atom would emit the photon of greatest frequency?
- n= 12 to n= 6
- n = 35 to n = 2
- n = 1 to n = 4
n = 2 to n= 9- n = 3 to n= 1
- n = 6 to n = 2
Question 4)
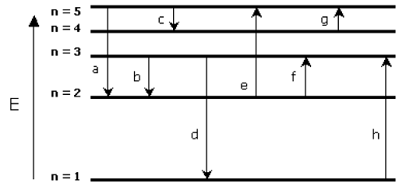
Below is the energy level diagram (not drawn to scale) representing the transitions made by an electron in a hydrogen atom that result in the observed lines of both the absorption and emission spectra. Some are in the visible region, and some are not.
4 different energy photons are represented (approximate wavelengths are given in parentheses):
infrared (~ 10e-4 m)
red (~ 10e-6 m)
blue (~ 10e-7 m)
ultraviolet (~ 10e-8 m)
Match the transition (a - h) with the photon described (approximate wavelengths are given in parentheses.) Your answer input should be a single, lower case letter.
(Please note: This is not a problem for which a calculator is required. Your knowledge of the Bohr model of the atom and the relative energies of transitions is all that is needed.)
Smallest energy emission
Answers:
Question 5)
List the types of electromagnetic radiation with frequencies higher than visible light. (Select all that apply.)
- x-rays
- ultraviolet light
- radio waves
- gamma rays
Question 6)
Two of the emission wavelengths in the hydrogen emission spectrum are 656 nm and 486 nm. One of these is due to the electron’s n= 4 to n = 2 transition, and the other is due to the electron’s n = 3 to n = 2 transition. Which wavelength goes with which transition?
The n = 3 to n = 2 transition produces the ________.
- 656 nm emission line
- 486 nm emission line
Question 7)
Which element burns with a characteristic bright red flame?
- strontium
- copper
- boron
- potassium
- sodium
Question 8)
Select the correct words to fill in the blanks:
In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, the n=5 to n=2 electronic transition corresponds with an ______ of energy; the change in the energy of the atom in this process is a _______ value.
- absorption, positive
emission, negative- absorption, negative
- emission, positive
Question 5)
List the types of electromagnetic radiation with frequencies lower than x-rays. (Please select all that apply.)
- infrared light
- microwaves
- gamma rays
- visible light
Question 7)
Which elements burn with a characteristic green flame? Please select all that apply
- sodium
- potassium
- strontium
- copper(II)
- boron
Question 8
Select the correct words to fill in the blanks:
In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, the n=1 to n=4 electronic transition corresponds with an ______ of energy; the change in the energy of the atom in this process is a _______ value.
- absorption, positive
- emission, positive
- absorption, negative
- emission, negative
Question 7)
Which element burns with a characteristic lavender (light purple) flame?
- potassium
- strontium
- copper
- boron
- sodium
Question 5)
List the types of electromagnetic radiation with frequencies lower than visible light. (Select all that apply.)
- ultraviolet light
- radio waves
- gamma rays
- x-rays






0 Comments